Genentech Announces New Data on Novel CD20-CD3 Bispecific Cancer Immunotherapies in People With Difficult-to-Treat Lymphomas
South San Francisco, CA -- December 7, 2019 -- Genentech, a member of the Roche Group (SIX: RO, ROG; OTCQX: RHHBY), today announced new data on two investigational CD20-CD3 T-cell engaging bispecific antibodies, mosunetuzumab and CD20-TCB, in people with relapsed or refractory (R/R) B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL). Results from the Phase I/Ib GO29781 study of mosunetuzumab, including data from people previously treated with chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy, will be presented at the 61st American Society of Hematology (ASH) 2019 Annual Meeting during the Plenary Scientific Session. The Plenary Scientific Session highlights the top six abstracts submitted to the meeting, as determined by the ASH Program Committee. Additionally, results from the Phase I/Ib NP30179 study evaluating CD20-TCB as a combination therapy with Gazyva® (obinutuzumab) for people with R/R NHL, will be presented.
“Despite recent treatment advancements, slow-growing and aggressive non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas present increasingly difficult management challenges with each subsequent relapse,” said Levi Garraway, M.D., Ph.D., chief medical officer and head of Global Product Development. “We’re encouraged by these early results, which suggest that our novel bispecific cancer immunotherapies may help people with relapsed or treatment-refractory disease who need more options.”
The GO29781 study evaluated mosunetuzumab in patients with R/R NHL, including patients who have relapsed following, or are resistant to, CAR T-cell therapy – a patient population with limited treatment options. Results from this dose-escalation study showed encouraging efficacy with an objective response rate (ORR) of 62.7 percent (n=42/67) in slow-growing NHL and 37.1 percent (n=46/124) in aggressive NHL. Additionally, data demonstrated a complete response (CR) rate of 43.3 percent (n=29/67) in slow-growing NHL and 19.4 percent (n=24/124) in aggressive NHL. CRs showed durability, with 82.8 percent (n=24/29) of patients with slow-growing NHL remaining in remission up to 26 months off initial treatment and 70.8 percent (n=17/24) of patients with aggressive NHL, remaining in remission up to 16 months off initial treatment. Of the participants who received prior CAR T-cell therapy, the ORR was 38.9 percent (n=7/18), and 22.2 percent (n=4/18) achieved a CR. Adverse reactions included cytokine release syndrome (CRS) in 28.9 percent of patients with 20.0 percent at Grade 1 and 1.1 percent at Grade 3. Grade 3 neurological adverse events occurred in 3.7 percent of patients.
Results from the Phase I/Ib dose-escalation NP30179 study, evaluating CD20-TCB at doses ranging from 0.6 mg to 16 mg plus Gazyva in people with R/R B-cell NHL, showed an ORR of 54 percent (n=15/28) and a CR rate of 46 percent (n=13/28). This included an ORR and CR of 66.7 percent (n=4/6) in people with follicular lymphoma and an ORR of 50.0 percent (n=11/22) and a CR of 40.9 percent (n=9/22) in aggressive NHL. The most frequently observed adverse event across all treatment doses was CRS, occurring in 67.9 percent of patients (n=19/28), with the majority of events being low grade (Grade 1-2).
Both mosunetuzumab and CD20-TCB continue to be evaluated in a robust clinical development program, investigating the treatments as monotherapies and in combination with other therapies, in people with slow-growing and aggressive forms of NHL.
About Genentech’s Investigational Bispecifics
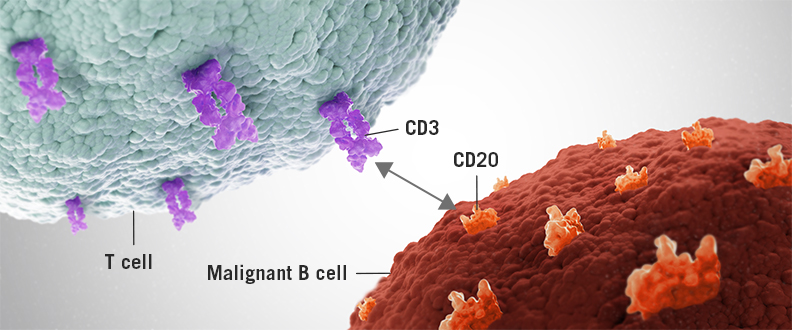
Genentech is currently developing two T-cell engaging bispecific antibodies, mosunetuzumab and CD20-TCB, designed to target CD20 on the surface of B-cells and CD3 on the surface of T-cells. This dual targeting activates and redirects a patient’s existing T-cells to engage and eliminate target B-cells by releasing cytotoxic proteins into the B-cells. Mosunetuzumab and CD20-TCB differ in their structures, and both are being developed by Genentech as part of our ongoing strategy to explore multiple bispecific formats, to identify those that maximize potential clinical benefits for patients. The clinical development programs for mosunetuzumab and CD20-TCB include ongoing investigations of these molecules as monotherapies and in combination with other medicines, for the treatment of people with CD20-positive B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas, including diffuse large B-cell lymphoma and follicular lymphoma.
About the GO29781 study
The GO29781 study [NCT02500407] is a Phase I/Ib, multicenter, open-label, dose-escalation study evaluating the safety and pharmacokinetics of mosunetuzumab in people with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Outcome measures include best objective response rate by revised International Working Group criteria, maximum tolerated dose, and tolerability.
About the NP30179 study
The NP30179 study [NCT03075696] is a Phase I/Ib, multicenter, open-label, dose-escalation study, evaluating the efficacy, safety, tolerability and pharmacokinetics of CD20-TCB. In this study, CD20-TCB is assessed as a single agent and in combination with Gazyva, following pre-treatment with a one-time, fixed dose of Gazyva, in people with relapsed or refractory B-cell non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma. Outcome measures include overall response rate, complete response rate per Lugano 2014 criteria, maximum tolerated dose, and tolerability.
About Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma
There are two main types of lymphoma: Hodgkin’s lymphoma and non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL). NHL has two subsets, aggressive and indolent (slow-growing).
NHL represents approximately 85 percent of all lymphomas diagnosed. According to the American Cancer Society, it is expected that nearly 74,000 people will be diagnosed with NHL in the United States in 2019, and nearly 20,000 will die from the disease.
Most cases of NHL start in B-lymphocytes, cells that are part of the body’s immune system and help to defend the body against infections. B-cell lymphoma develops when these cells become cancerous and begin to multiply and collect in the lymph nodes or lymphatic tissues such as the spleen. (Article from : www.drugs.com)

